Overview of iNonius Speed Test
This speed test site enables Internet users to measure various qualities of their Internet environment. Each user can see the visualized result in the browsers.
Measurement Menu
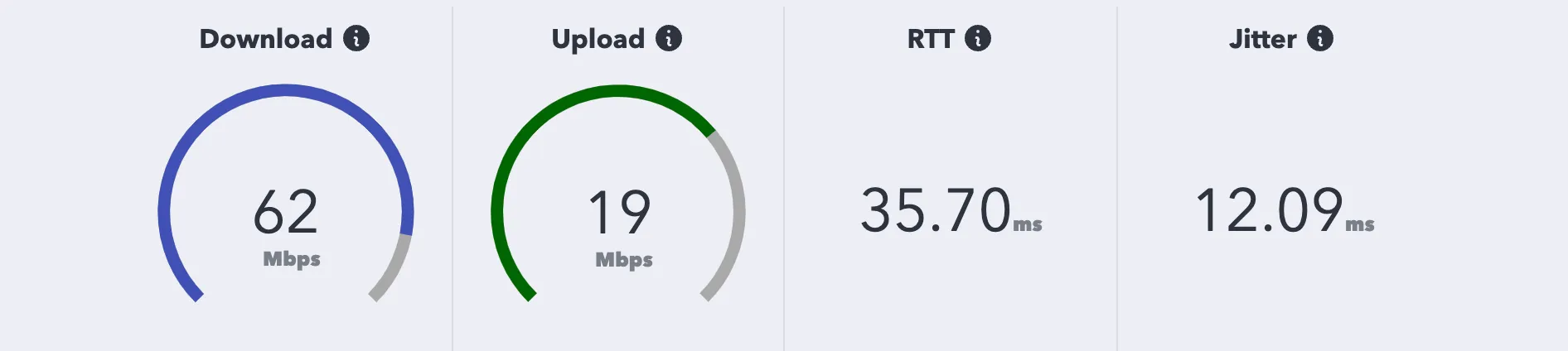
Download
Download means your computer receives data from the iNonius server. High download speed (bps) makes it easier to watch videos, and allows you to receive big files such as games and OS updates in a short time.
[Measurement Method]
Your browser sends a HTTP GET request to iNonius server and receives 100M Byte of random data from the server. It repeats continuously for 15 seconds. If download speed is fast, it ends without continuing 15 seconds. During the measurement, your browser keeps updating the speed meter.
Upload
Upload means your computer sends data to the iNonius server. If the upload speed (bps) is high, you can send videos, photos, files, etc. to the cloud in a short time.
[Measurement Method]
Your browser sends a HTTP POST request composed of 20M Byte of random data to iNonius server. It repeats continuously for 15 seconds. If download speed is fast, it ends without continuing 15 seconds. During the measurement, your browser keeps updating the speed meter.
RTT
RTT (round trip time) is the round trip time between your computer sending data to the iNonius server and receiving the response. Same meaning as “latency”, “lag” or “delay”. A short RTT means each person’s voice can be reached quickly to the others in an online meeting, which reduces audio collisions.
[Measurement Method]
The browser measures the time between sending a HTTP GET request instead of regular ICMP ping to the iNonius server and receiving its response. It repeats it 10 times and shows the minimum.
Jitter
Jitter is a dispersion of the results of multiple RTT measurements. Jitter is generated by various factors along the communication path. High jitter leads to unstable quality.
[Measurement Method]
This system calculates Jitter by weighted averaging the results of the 10 RTT measurements.
Requirement of your environment
Requirements of your environment are as follows.
- Internet connectivity
- Web browsers on PC, Smartphone, Tablet, etc.
Measurement Flows
iNonius server automatically measures all measurements after one-clicking / tapping the start button.
- Firstly, iNonius server measures the RTT, Jitter.
- Secondly, it measures Download speed.
- Finally, it measures Upload speed.
These measurements will be taken with IPv6 or IPv4 used to connect to this measurement site. After these are completed, if the user’s network has connectivity with the other version of IP (IPv4 or IPv6), the same measurements will automatically start with that version of IP.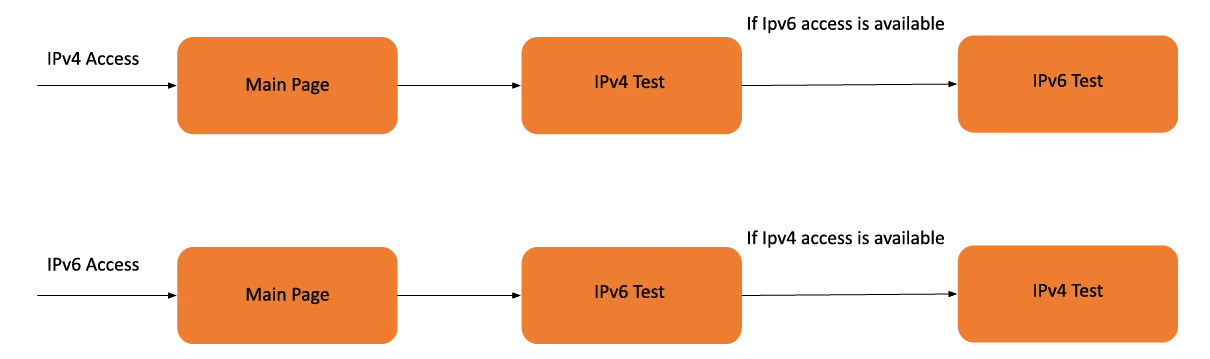
Measurement Section
This system measures the section from the client to the measurement site in Otemachi Tokyo. Therefore, the environment included in the measurement results will vary depending on the user, such as wired or wireless sections.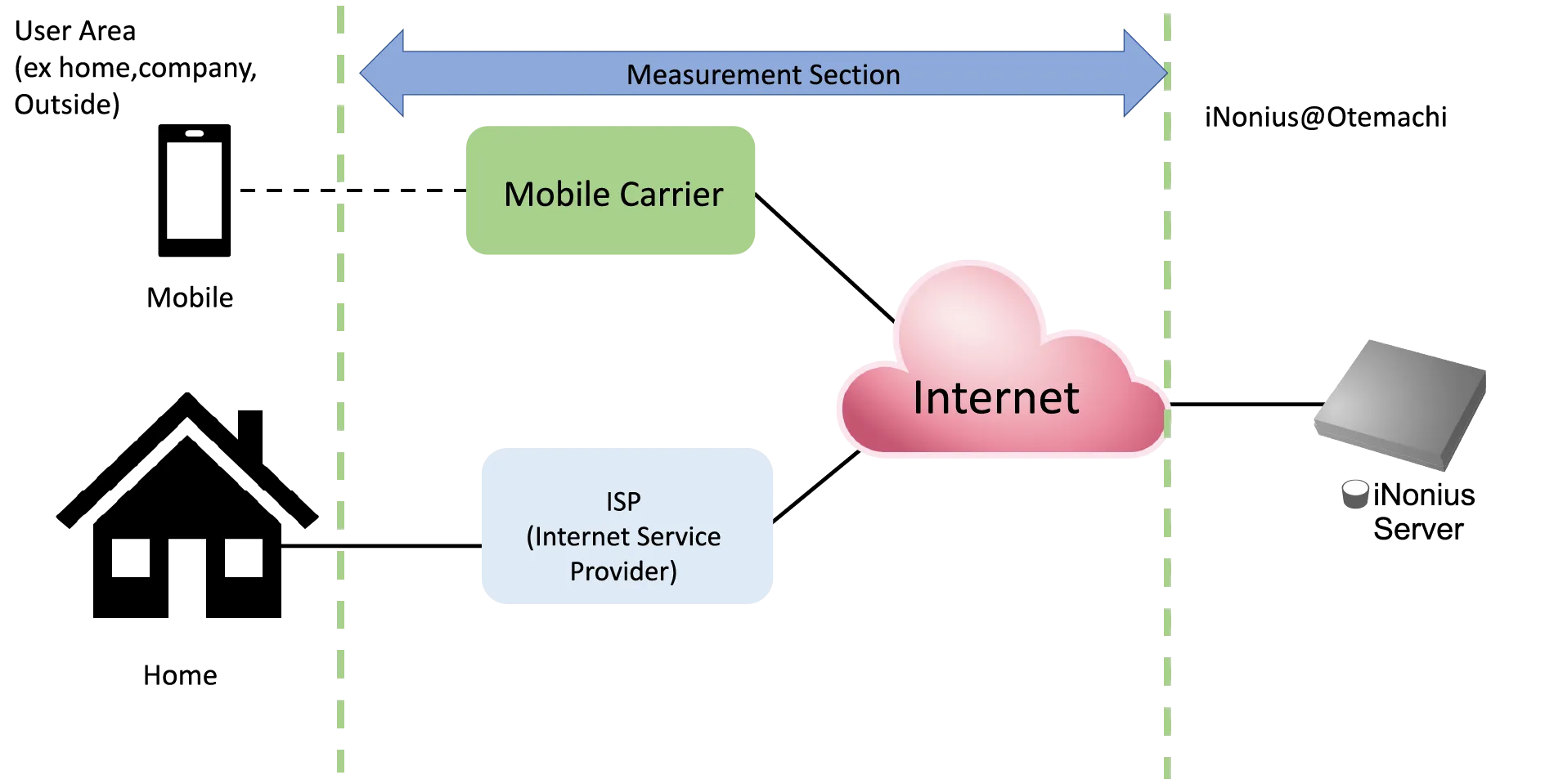
Required Measurement Time
iNonius server measures for approximately 30 seconds each IPv4 and IPv6.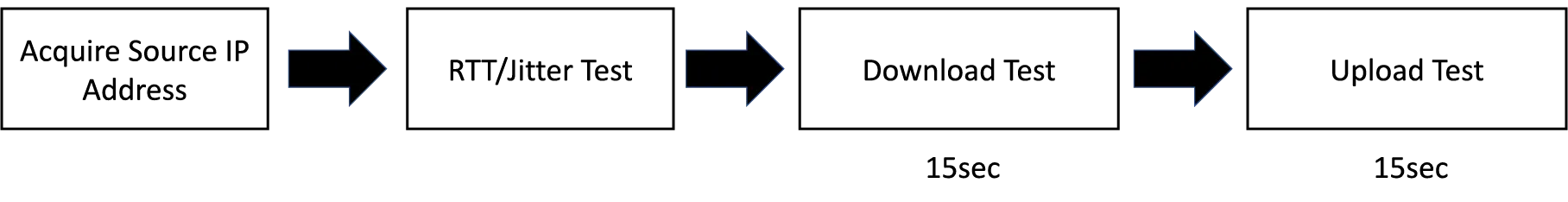
Network Configuration
iNonius server is located on the network of Cloud and SDN Laboratory (AS7530) in Otemachi Tokyo. This network (AS7530) has some Internet connectivities. One is BroadBand Tower (AS9607) as a transit, and others are JPIX and DIX-IE as IXs (Internet Exchangees). When measuring at this site, your packets go through one of these routes.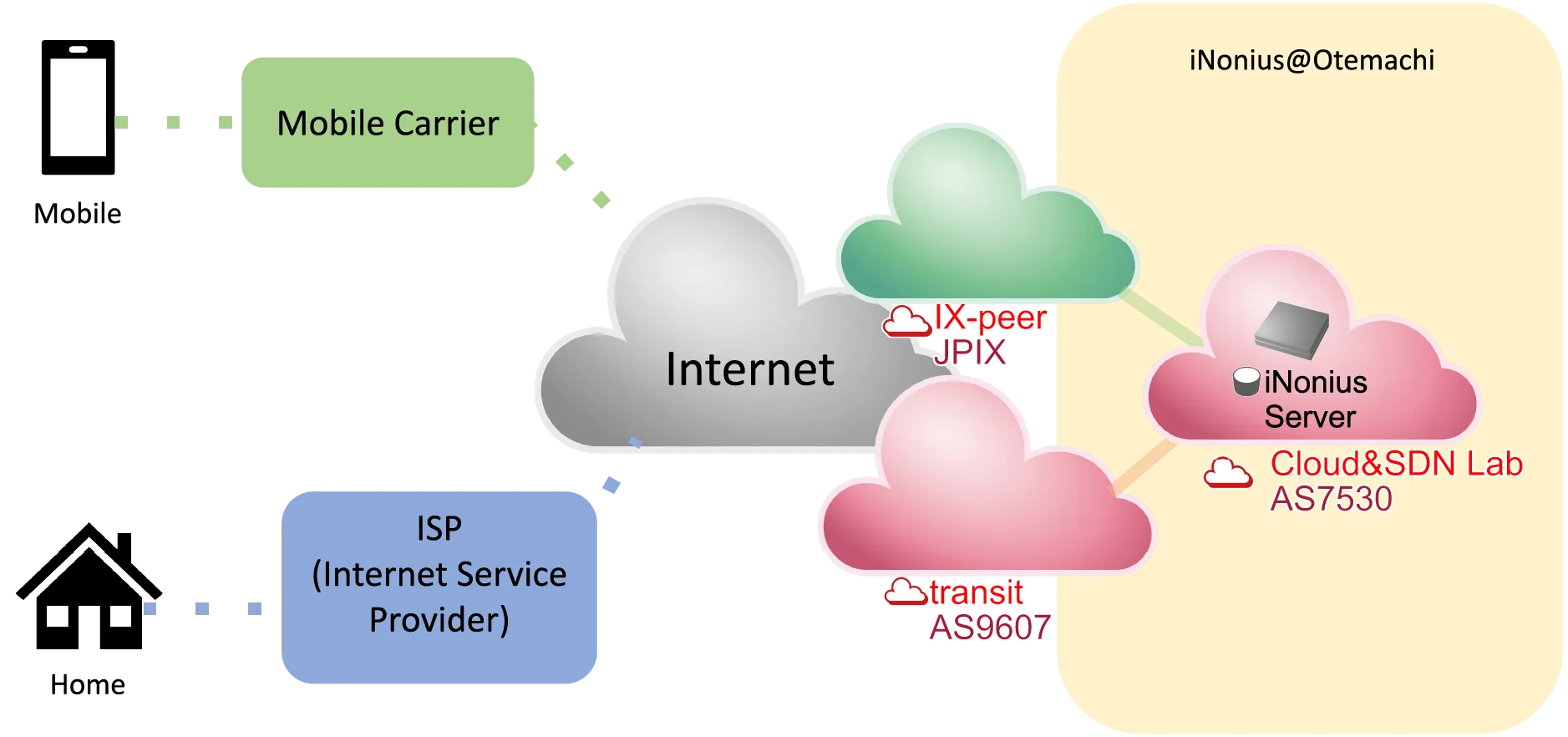
Terms
IP address
IP Address is an universal identifier that distinguishes each device on the Internet.
IPv4
IPv4 Address is one of the versions of IP addresses which has been used since the beginning of the Internet. The stock of IPv4 addresses exhausted in 2011, since there are only 4.3 billion addresses. Since then, network providers around the world have introduced IPv4 Address Sharing Systems for using a single IPv4 address with multiple Internet users.
IPv6
IPv6 Address is the successor to the exhausted IPv4 address. The number of IPv6 addresses is approximately 340 undecillion (340 trillion trillion trillion) (3.4×10^38), and it is going to be the mainstream address. People around the world have started to use IPv6 in addition to exhausted IPv4.
Transit
This is the connectivity provided by other organizations to connect your network to the entire Internet.
Internet Exchange
IX (Internet Exchange) is the intersection where physically connected content providers, ISPs and others could exchange their traffic. 2 parties virtually connected through IX can exchange their traffic. It is also called IXP (Internet Exchange Point).
bps
It is a unit that represents the communication speed in the network. It means the number of bits that are transmitted per second (Bits Per Second).
Disclaimer
When you measure on this site, iNonius server will acquire your global IP address. The iNonius Project may use this IP address as statistical information that does not identify each user. iNonius Project will not use it for any purpose other than this purpose.
iNonius server uses “Google Analytics” as an analysis tool. This Google Analytics uses cookies to collect data. These data are collected anonymously and are not personally identifiable. You can disable this function. See your browser settings. Details are on Google Policy and Terms.
The internet communication charges of each user shall be owned by each user.
iNonius Project does not accept inquiries about this site.
This project and each member of the project will not take any responsibility for this site, such as any damages caused by the measurement.